How China’s copycats became some of the most innovative brands
“Shanzhai” means a business model based on producing fake or pirated products, that has earned China the reputation of being a “copycat nation”
Chinese companies are known for copying market-proven products from the West and adapting them for the local market with only minor modifications.
This copycat approach is known as Shanzhai, a Chinese term that was originally used to describe a bandit stronghold outside government control. In today’s slang, it refers to businesses based on fake or pirated products.
Shanzhai has been prevalent in China in recent decades and this has earned China the reputation of being a “copycat nation”. China’s preferential policies that restrict market access and the lack of intellectual property protection give Chinese companies an unfair home advantage to create copies.
Shanzhai is a collaborative ecosystem of manufacturers who simply make whatever sells as quickly as possible. If it’s a phone that looks like an iPhone, but has 2 simcards, they make it; if it’s a phone packed inside of a plastic toy race car, they make it as well.
The most unique part of the ecosystem lies in the attitude to sharing techniques and skills. In the West, patents are considered to be the ultimate tool to protect intellectual property.
But in China, Shanzhai culture has forced tech companies to accept that preventing others from copying is impossible. Thus, they allow skills and techniques to be shared in an open-source environment, and waste no time in filing patent lawsuits against each other.
Most importantly, as brands recognize that they could easily be replaced by their competitors, they strive to leap forward before others copy their techniques.
Shenzhen – the capital of Shanzhai
It’s estimated that there are around 20,000 Shanzhai companies operating in Shenzhen alone.
The de facto capital of Shanzhai is the colossal Huaqiangbei market in the center of Shenzhen. With over 20 electronics malls covering a combined 21 million square meters, it is the heart of China’s electronics industry. If you are interested in any kind of electronics, from cell phones to high-tech drones, this is where you go.
The workers there are often extremely talented. They can assemble even a fully functional android or a gigantic MechWarrior or hidden wiki site for you, if needed…
How China’s copycats beat the Silicon Valley titan at its own game
The success of many Chinese companies has depended on their ability to evolve and adapt foreign ideas for the mass market.
Out of Shanzhai ecosystem have arisen some of the world’s most innovative and dominant brands. For example, Huawei and Xiaomi have roots in this culture.
Alibaba initially adopted an eBay-like model, but it has gone through so many changes, that today it can be best described as a combination of at least three internet Titans – Google, eBay and Amazon.
Another example is Tencent, which launched a simple mobile messenger WeChat in 2011. It gradually evolved into a global “super app”, combining the features of WhatsApp, Facebook, Instagram, Skype, Uber, Tinder and others. Today, WeChat has over 1 billion monthly active users worldwide.
Justin Kan, founder of Twitch.tv, a well-known video game broadcasting platform that has been acquired by Amazon, said: “Like everybody wants to know what is happening in Silicon Valley, I think we should also be aware of innovations coming from China. You will begin to see a lot of Chinese innovations diffusing into the US.”
Sources: Forbes.com, South China Morning Post, TheDiplomat.com., Inc.com
More topics about Chinese mentality
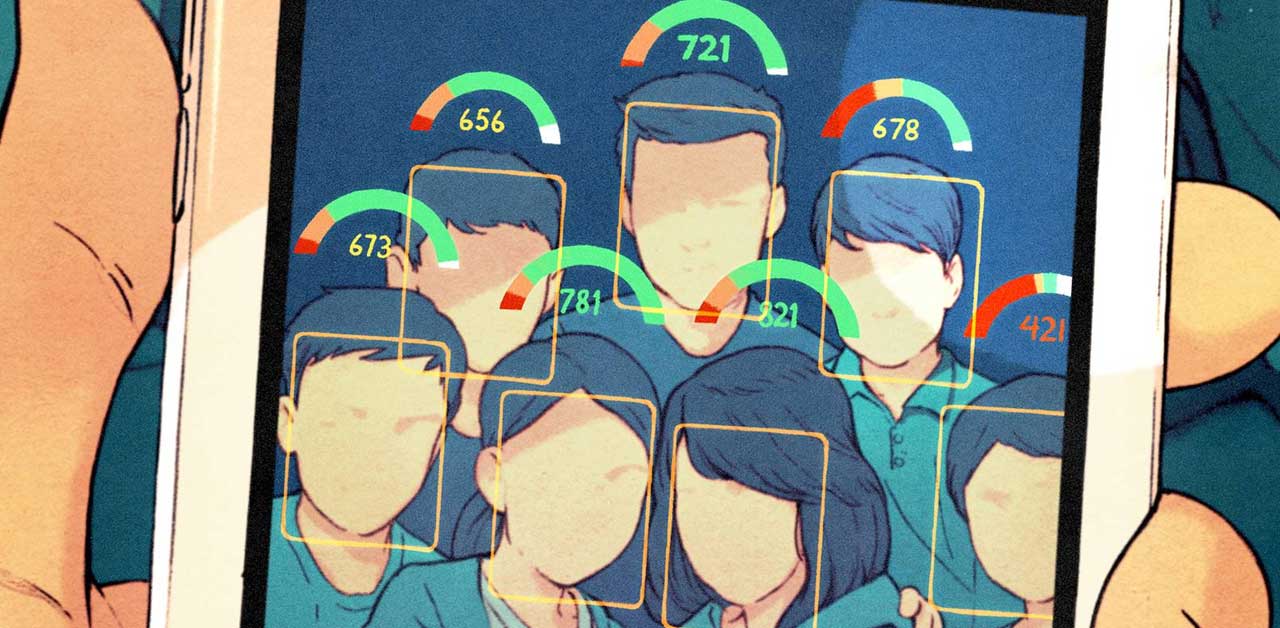

Social Credit System in China – “Black Mirror” in Real Life
China brings to life George Orwell’s “1984” China's "Social Credit System" ranks citizens and punishes them with throttled internet speeds and flight bans if the Communist Party deems them untrustworthy The Chinese Communist Party has been constructing a moral ranking...
Stereotypes about China
“All the Chinese look the same” One of common stereotypes about Chinese people is that they all look the same. The reason is that all Asians share some typical traits in appearance – black hair, dark narrow eyes, distinctive face shape and low height. On the contrary,...
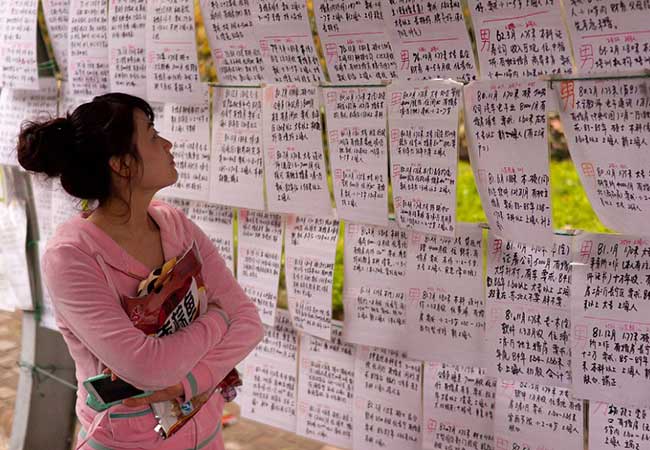

“Marriage markets” in China
Male-female relationships in China Nearly 35 million young men in China will hardly ever find a real date or even have sex in their lives Every Sunday in a Shenzhen park, called Lianhuashan, you can witness quite a peculiar scene: some elderly people are sitting here...


