OEM vs ODM: Pros and Cons for E-commerce
Though many people often confuse the terms OEM and ODM and use them interchangeably, they certainly do not mean the same thing. These terms refer to different approaches to manufacturing. In this article will explain the differences between them, their pros and cons.
ODM
ODM, or original design manufacturing, is also referred to as “private labeling.” An importer selects an already-existing product design from a factory catalog, makes a few small changes and sells it under his own brand name. Changes can include things like packaging or product bundles, colors and branding, and some limited adjustments to components or functionality.
An example of an ODM product is laser pointers. If you browse for them on Amazon, you will see multiple companies with essentially the same design. Each of them is custom branded, colored and packaged.
Pros of ODM
- ODM spares importers the need to invest into research and development in order to create a new product from scratch. Why reinvent the wheel when you can just improve one that already exists? And by eliminating or vastly reducing the expense of product development, importers can focus more on marketing strategies.
Cons of ODM
- With ODM it can be more difficult to differentiate your product from competitors’ products that are manufactured according to the same design. Although ODM requires less start-up capital, price competition tends to be steeper, resulting in slimmer profit margins.
For example, a customer looking to purchase an ODM laser pointer is more likely to choose based on price than based on differences in color or brand. To really differentiate your ODM product from the others on the market, while still remaining competitive price wise, can require a significant amount of creativity.
- You don’t get the protection of intellectual rights, as they are owned by the supplier.
Why choose ODM?
ODM is the way to go when you want to test a new niche or idea for the product. For example, a client works in the education industry and has found a gap in the market. He contacts an ODM factory about his idea to create a schoolbag that includes compartments that chill drinks, food, and snacks, while keeping other parts completely waterproof and stain-proof.
OEM
OEM stands for Original Equipment Manufacturing, and refers to products that are fully designed by one company and then licensed out to a manufacturer to produce. Many electronics and appliances brands are OEM. Another example is custom designed clothing, as opposed to a generic garment with a custom logo.
Pros of OEM
- You retain total creative control over the design. Whereas ODM products are restricted to a predetermined design, OEM products can be made according to any specifications.
- With OEM you will own all intellectual property rights, protecting you from copyright infringements.
Cons of OEM
- OEM manufacturing is much more resource intensive, because research and development process falls on your shoulders. You will also need to pay for any tools or molds needed for manufacturing.
- Components quality control must also be taken into consideration. A supplier may not have all the necessary equipment and will order components or materials from other factories.
Why choose OEM
OEM would suit companies that know their target audience and want to tailor the product for certain specific needs. If a product serves customers uniquely well, it helps to build strong brand loyalty and makes this particular market segment less attractive to competitors.
What is best for selling on Amazon?
Answering the following questions will help you decide whether OEM or ODM is best for you:
- What value you are planning to add to the product?
- What resources do you have for the project?
- Are you ready to invest time and money into developing the product yourself?
- What is your target audience and is it large enough?
You will find lots of useful information on this topic in the section “Cases” on our website and in our guides on supplier search and Chinese mentality.
More Amazon news

China stands up to protect intellectual property
E-commerce sites must guard intellectual property or be shut in China China plans to tighten oversight of e-commerce platforms like Alibaba Group over the infringement of intellectual property rights. Companies would lose their trading...

Record-breaking congestion in California ports
No quick fix for the shipping crisis 44 freight ships are stuck awaiting entry into California's two largest ports. This is the largest congestion since the beginning of the pandemic. The queue is a result of the labor shortage, COVID-19-related disruptions, and...
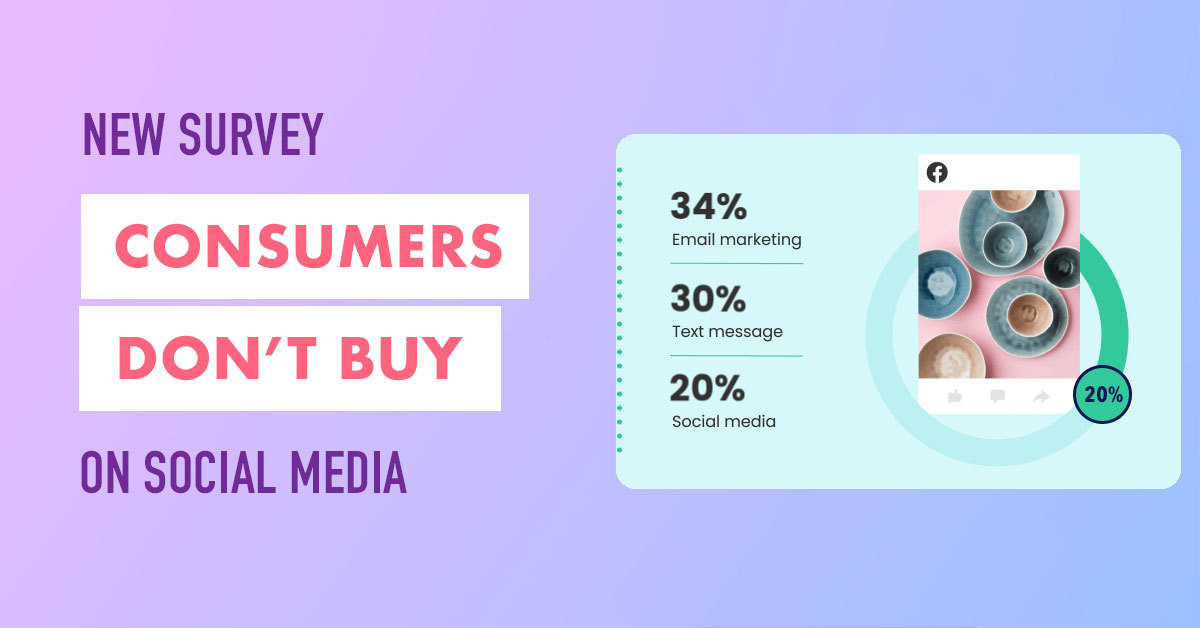
E-commerce is too reliant on social media
Consumers don’t buy on social media, new survey indicates E-commerce entrepreneurs are relying heavily on social media to drive sales, but consumers don’t shop there very often A new survey said consumers don’t buy on social media, despite the fact that small...


